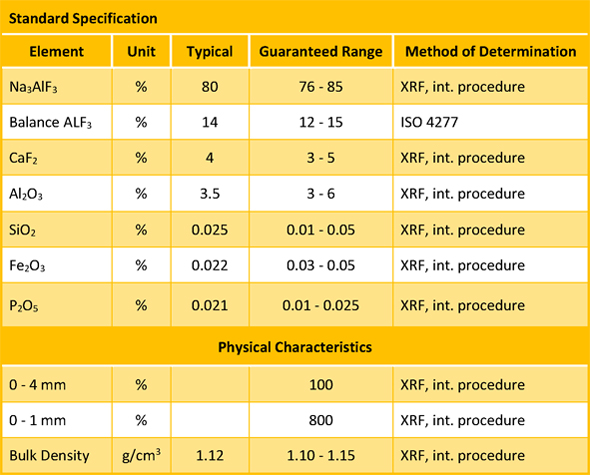
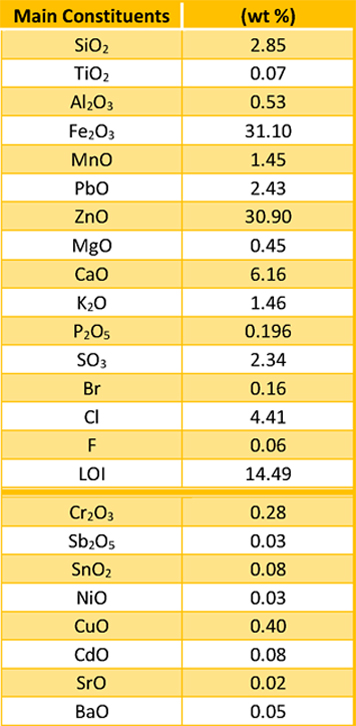
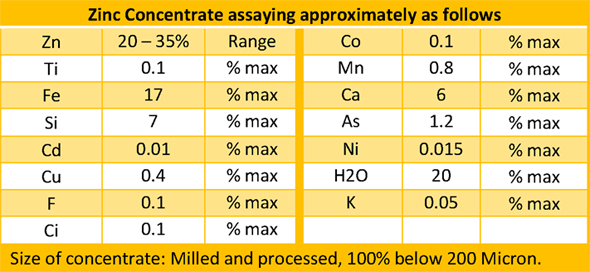
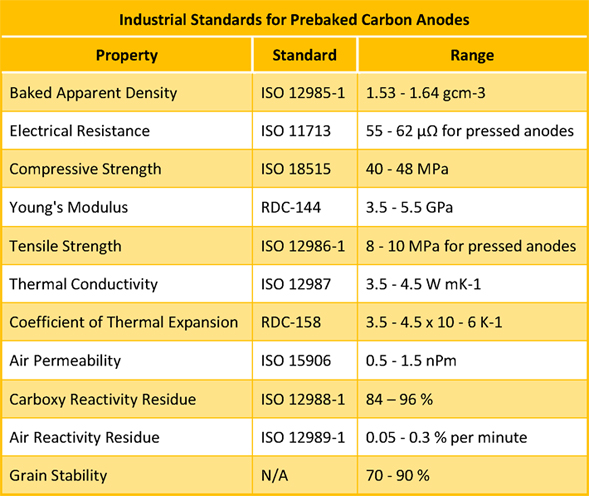
Graphite electrodes serve to transfer the electrical energy from the power supply to the steel melt in the EAF bath. They are typically made using premium petroleum needle coke, coal tar pitch, and some additives.
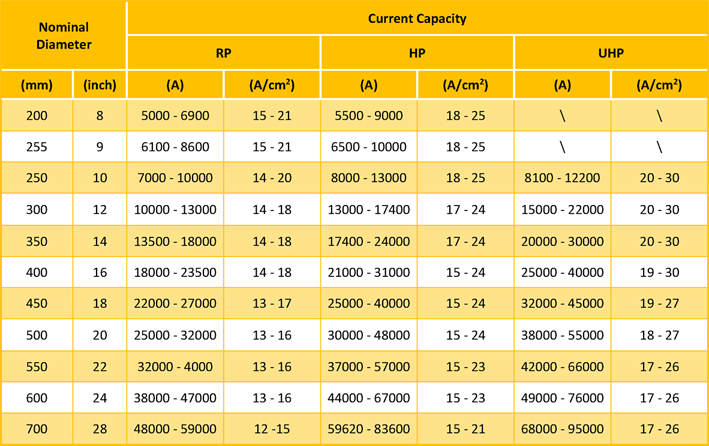
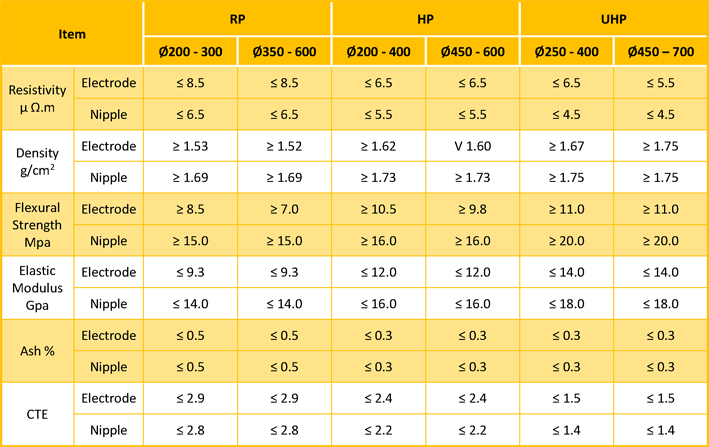
Electrode consumption varies between 1.8 and 9.9 kg/t of liquid steel (Parkash, 2010) depending on the process characteristics and electrode quality. Ameling et al. (2011) reported that the electrode consumption in Germany in 2010 was approximately 1.1 kg per ton as a result of the reduction of time between the taps to 40 min and consequently the lower electricity consumption (345 kWh/t). Electrodes are classified as regular grade or premium grade on the basis of their physical properties (International Iron and Steel Institute, 1983).
For DC Furnaces (direct current furnaces) / Size: 22-32 inches
Electrodes for DC furnaces, which require 1 column of graphite electrodes. High maximum current density. The diameter of these electrodes is getting bigger: the current maximum diameter is 32 inches (801 mm).
For AC Furnaces (alternating current furnaces) / Size: 16-28 inches.
Alternating current furnaces require 3 columns of graphite electrodes. They mostly use 20-28 inch electrodes, the standard size in electric furnaces.
For LF Furnaces (refining furnaces) / Size: 10-18 inches
These electrodes are for refining materials like molten steel. LF Furnaces have a smaller capacity than DC.
 English
English
 Persian (Iran)
Persian (Iran)